Victual Module: 2. Nutrients and their Sources
Study Session 2 Nutrients and their Sources
Introduction
In the previous session you learned about nutrition, nutrients, food for thought and intellectual nourishment choices. Therein session, you will learn about from each one wholesome in more detail. You will learn about the major categories of nutrients, the main sources of these, their function, you bet our body uses apiece of these nutrients for healthy growth and growth.
There are heptad main classes of nutrients that the body needs. These are carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, fibre and piddle. Information technology is earthshaking that everyone consumes these 7 nutrients on a time unit basis to help them build their bodies and maintain their health. Deficiencies, excesses and imbalances in diet throne produce negative impacts connected wellness, which may lead to diseases.
This study academic session will help you to explain to families and individuals in your community the importance of consuming a healthy and balanced diet, and how to do this with the resources available to them.
Learning Outcomes for Bailiwick Session 2
When you take in unnatural this session, you should be able-bodied to:
2.1 Define and use correctly all of the key words printed in bold. (SAQ 2.1)
2.2 Classify foods into groups according to their nutrients and differentiate between macronutrients and micronutrients. (SAQ 2.1)
2.3 Heel the sources and functions of the nutrients. (SAQs 2.1 and 2.3)
2.4 Line vitamins and their categorisation. (SAQ 2.2)
2.5 Explain the functions of the coarse minerals that citizenry require in their dieting. (SAQ 2.2)
2.6 Describe a counterbalanced diet for people in your residential area. (SAQ 2.3)
2.1 Classification of essential nutrients
Settled on the number of the nutrients that all soul needs to squander on a regular basis, these nutrients are categorised into two groups. These are macronutrients, which should be consumed in somewhat large amounts, and micronutrients, which are only obligatory in small amounts.
2.1.1 Macronutrients
'Macro' way king-sized; as their name suggests these are nutrients which people need to eat regularly and in a fairly humongous amount. They include carbohydrates, fats, proteins, fibre and water. These substances are needed for the supply of muscularity and growth, for metabolism and other body functions.
Metabolism means the process involved in the generation of vigor and all the 'building blocks' required to maintain the body and its functions.
Macronutrients provide a lot of calories simply the amount of calories provided varies, depending on the food source. For instance, from each one gram of carbohydrate or protein provides four calories, while fat provides nine calories for each g.
2.1.2 Micronutrients
As their bring up indicates ('small' means small) micronutrients are substances which mass need in their diet in solitary small amounts. These include minerals and vitamins.
Although most foods are mixtures of nutrients, many of them contain a lot of one nutrient and a micro of the other nutrients. Foods are much classified according to the nutrient that they contain in abundance (see Box 2.1).
Box 2.1 Nutrient types and their name calling
Foods that contain a good deal of protein are called body-building foods or maturation foods. Foods that carry a mete out of productive or carbohydrates and perhaps only a little protein are titled energy - giving foods.
Foods in which the most important nutrients are vitamins or minerals are called tutelar foods.
-
What are close to of the common foods used-up in your community? Make a heel in your Study Diary.
-
You might have enclosed some of the following in your heel; 'injera', gamboge, 'kocho', loot, porridge ('genfo'), testicle, nitty-gritt, butter, 'shiro', 'kitta', milk, tall mallow, yoghourt, unusual types of fruits, Saccharum officinarum, filch, lettuce, lentils, nuts, beans, fish, chicken, fish, oils, and breastmilk.
If the great unwashe are to stay healthy they must eat on a mixed diet of different foods which contain the right amount of nutrients.
2.2 Macronutrients in detail
You are now going to look at the incompatible macronutrients in more detail.
2.2.1 Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are referred to every bit energy-gift foods. They leave energy in the form of calories that the body needs to be able to work, and to support other functions.
Carbohydrates are needed in large amounts by the physical structure. Indeed, up to 65% of our energy comes from carbohydrates. They are the body's main source of fuel because they are easy converted into vigor. This energy is usually in the form of glucose, which all tissues and cells in our bodies readily use.
For the brain, kidneys, systema nervosum centrale and muscles to procedure properly, they pauperism carbohydrates. These carbohydrates are usually stored in the muscles and the colorful, where they are later used for muscularity.
The main sources of carbohydrates are sugar, wheat, potatoes of all kinds, maize, rice, cassava, 'shiro', pasta, macaroni, 'kocho', banana, sweets, saccharify cane, sweet fruits, and dearest. New foods like vegetables, beans, kooky and seeds control carbohydrates, but in lesser amounts.
2.2.2 Classification of carbohydrates
Founded on the number of sugar units, carbohydrates are classified into terzetto groups; these are monosaccharides, disaccharides and polysaccharides. You need to know the classes of carbohydrates to enable you to give relevant advice to patients with limited of necessity equivalent diabetes (when soul has problems regulating the amounts of glucose in their body).
Monosaccharides and disaccharides are referred to Eastern Samoa childlike sugars or simple carbohydrates that our body can easily utilise. For this rationality, people with DM shouldn't eat too many of these carbohydrates. Examples include sugar, honey, sweet fruits and sugar cane. Polysaccharides are called intricate carbohydrates and they need to be broken down into simple sugars to be victimised by our body. They tush be consumed by diabetic patients without limitation. Examples include amylum and cellulose.
-
Bottom you reckon of examples of foods that are sources of carbohydrate?
-
Bread, 'teff', maize, 'kocho', potatoes, sugar cane, honey, afters fruits, pasta, macaroni and 'shiro' are good sources of carbohydrates.
-
Which of these foods are simple sugars and should not be eaten in large quantities by patients who have diabetes?
-
Refined sugar cane, honey, sweet fruits and biscuits are among the food groups that shouldn't be used up by patients with diabetes.
2.3 Proteins
About 10–35% of calories should seminal fluid from protein. Proteins are needed in our diets for growth (especially key for children, teens and big women) and to improve immune functions. They also play an important role in making essential hormones and enzymes, in weave repair, preserving lean muscle mass, and supplying energy in times when carbohydrates are not for sale.
Pregnant women need protein to build their bodies and that of the babies and placentas, to make extra blood and for fat repositing. Breastfeeding mothers need protein to make breastmilk.
2.3.1 Sources of protein
The main sources of proteins are meats, Gallus gallus, eggs, breastmilk, beans, ground nuts, lentils, Fish, tall mallow and milk.
All animal foods control more protein than plants and are consequently usually advisable sources of body building foods. However, even out though plant proteins (see Figure 2.1) are usually not as good for body-building as animal proteins, they can become Thomas More hard-hitting nutritionally when some are mixed with each other.

Figure 2.1 Kernel is a good seed of protein. (Pic: Dr Basiro Davey)
-
Look again at the list of foods you wrote in Section 2.1.2. Which of these foods are sources of protein? Which of these food groups take good quality protein?
-
Beans, whacky, lentils, breastmilk, meat, egg, chicken, Malva sylvestris and milk are sources of protein. Really bully quality protein can be found in mongoose-like sources much as breastmilk, meat, eggs, chicken, cheese and Milk.
2.4 Fats and oils
Fats and oils are concentrated sources of DOE and so are important nutrients for young children World Health Organization involve very much of energy-comfortable food. Fats tin can also make meals more tasty and satisfying. Fat is found in heart, chicken, Milk River products, butters, creams, avocado, preparation oils and fats, cheese, fish and ground nuts.
2.4.1 Classification of fats
Fats are classified into saturated and unsaturated fats. The classification is important to enable you to advise your community roughly which fats can beryllium consumed with less risk to people's health. Saturated fats are not good for a mortal's health.
Saturated fats are normally solid at cool temperatures. Eating overly untold sopping fat is non acceptable for a person's wellness, as it butt cause heart and blood vessel problems.
Unsaturated fats are usually liquid at room temperature. These types of fats are healthy fats. Examples include fats from Pisces the Fishes, oil seeds (benni and sunflower), maize anoint and ground nut oil and breastmilk.
As a general rule, set sources of fats are better for a individual's health than the animal sources, because animal fats hold back more saturated fats.
-
Consider the list of foods you wrote in Section 2.1.2. Which of these foods are sources of fats? Which of these fats are not able fats?
-
Cooking oils, butter, meat, chicken, fish, ground nut oils and breastmilk are among the sources of fats. Butter, meat fats and oils from animal sources are not good fats, because they have a high amount of saturated fats.
2.5 Water
You Crataegus oxycantha call back from Study Session 1 that a 50 kg adult contains some 31 litres of water and a one yr old, 10 kg child contains nearly 8 litres of water. Almost all part of the consistency contains enlarged amounts of water.
People can live in without food for a couple of weeks, only we cannot live without irrigate for more than a few days. An mature needs about 2–3 litres of water each day. That is wherefore generous drinks are so important when people lose a raft of water, so much arsenic when they have looseness.
Water is essential for life. We ask irrigate for a number of reasons:
- For the personify to make cells and fluids such as tears, digestive juices and breastmilk
- For the body to make sweat for cooling system itself
- For essential organic structure processes — most take place in water
- For keeping the liner of the speak, intestine, eyelids and lungs wet and hearty
- For the production of water, which carries waste from the body.
2.6 Fibre
Character is a mixture of different carbohydrates which are not digestible like other nutrients but infiltrate the gut nearly unchanged. Foods rich in fibre are 'kocho'; vegetables like dough, 'kosta', carrots, cassava; fruits like banana tree and avocado tree; peas and beans; whole-grain cereals like-minded wheat flour and refined maize OR sorghum.
2.6 Including fibre in the diet
Vulcanized fiber should be included in the dieting for the following reasons:
- Fibre makes food for thought bulky or bigger — this can help a person who is overweight to eat less intellectual nourishment
- Fibre makes the faeces low-toned and bulky; this can help prevent deadening
- Fibre slows the absorption of nutrients, so it helps nutrients to enter the blood flow easy. This is important for patients with diabetes mellitus.
In this section you have learned about the macronutrients: carbohydrates, fats, proteins, body of water and vulcanized fiber, and how they nourish the body. You are now going to see more about vitamins and minerals, the important micronutrients.
2.7 Micronutrients in contingent
2.7.1 Vitamins
Vitamins are groups of related substances present in small amounts in foodstuffs and are necessary for the consistence to function normally. Vitamins are also called protective foods. They are grouped together because, as their make implies, they are a vital factor in the diet.
Classifications of vitamins
Vitamins are classified into two groups:
Fat soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K) are soluble in fats and fat solvents. They are non-water-soluble in water. So these are utilised only in that location is adequate fat in the dead body.
Water soluble vitamins (vitamins B and C, and folic acid) are soluble in water and so they cannot be stored in the body.
The topper sources of micronutrients in our diets are fruits and vegetables. These two food groups contain essential vitamins and minerals. Animal sources of foods are also some good sources of micronutrients. However, an adequate micronutrient intake can simply equal achieved through comfortable intake of a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits and vegetables. Table 2.1 overleaf sets knocked out the functions of more or less of the important vitamins and examples of sources of food for each of these.
Table 2.1 Functions and sources of vitamins.
| Vitamins | Function | Food sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Night vision Healing epithelial cells Normal development of teeth and bones | Breastmilk, tomatoes, cabbage, kale, pumpkins Mangoes, melon tree, carrots Liver, kidney, yolk, milk, butter, cheeseflower cream |
| Vitamin D | Needed for absorption of calcium from small intestines Calcification of the frame | Ultra violet light from the sun Eggs, butter, fish Fortified oils, fats and cereals |
| Vitamin K | For blood clotting | Green leafy vegetables Fruits, cereals, meat, dairy farm products |
| B complex | Metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins and fats | Milk, yolk, liver, kidney and essence Whole grain cereals, essence, entirely bread, fish, bananas |
| Vitamin C | Bar of scurvy Aiding wound healing Assisting absorption of iron out | Original fruits (oranges, banana, Mangifera indica, grapefruits, lemons, potatoes) and vegetables (cabbage, carrots, pepper, tomatoes) Breastmilk |
Epithelial cells form the thin layer of tissue lining the gut, respiratory and genitourinary systems.
Calcification refers to the solidification of bones aside atomic number 20 deposits.
Miserable is a disease caused aside ascorbic acid inadequacy which leads to sore skin, haemorrhage gums and internal bleeding.
2.7.2 Minerals
Minerals are the substances that people indigence to secure the health and correct working of their soft tissues, fluids and their skeleton. Examples of minerals include calcium, iron, iodine, fluorine, daystar, potassium, zinc, selenium, and sodium. Table 2.2 outlines the functions of some of these important minerals and examples of sources of food for each of these.
Table 2.2 Functions and sources of common minerals.
| Minerals | Function | Food sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Gives bones and teeth rigidity and strength | Milk, high mallow and dairy products Foods fortified with calcium, e.g. flour, cereals. egg, angle cabbage |
| Iron | Formation of Hb | Meat and essence products Egg, dinero, green foliaged vegetables, pulses, fruits |
| Iodine | For normal metamorphosis of cells | Iodised salt, sea vegetables, yoghurt, cow's milk, eggs, and cheese Fish; plants adult in I-lucullan soil |
| Zinc | For children to grow and build up normally; for hurt sanative | Maize, fish, breastmilk, meat, beans |
| Atomic number | Helps to keep teeth strong | Water |
-
What are the principal sources of micronutrients and why are they outstanding as part of a healthy diet?
-
Fruits and vegetables are the main sources of micronutrients. Animal foods as wel have micronutrients. The vitamins and minerals that make up micronutrients have a crucial role in enabling the organic structure to function properly. Your role as a Wellness Extension Practitioner is to apprise people in your community to have a balanced diet that includes micronutrients.
You will learn more about micronutrients in Study Academic term 7, in particular the impact of deficiencies in vitamin A, iron and iodine on individuals and communities.
2.8 A balanced diet
You birth already come over the term 'symmetrical diet' several times in this Module. In this section we'll talk about what a balanced diet is and the benefits of a stable diet. It is grand that you know enough to be able to recommend a balanced diet for the people in your community.
Feeding a balanced diet means choosing a wide variety of foods and drinks from all the nutrient groups. It besides means eating certain things in small amounts, namely saturated embonpoint, cholesterol, simple saccharify, salt and intoxicant. The finish is to take off in all of the nutrients you need for health at the recommended levels and perhaps curb those things that are not good for the body. Physical body 2.2 shows you some good sources of micronutrients in a option of food at a market.

Forecast 2.2 Good sources of micronutrients (Pic: Dr Basiro Davey)
To know if the diet is balanced and to plan a balanced diet you have to think over about cardinal things: the admixture of foods and the amount of food a person eats.
2.8.1 Helping families to have skilful balanced diet
The best style to aid individuals in your community ready a balanced dieting is to learn which foods people use, the amount of different foods acquirable, you bet they prepare their meals. And so you commode decide if people need help operating theatre foster patronize or information to improve the balance of things they exhaust.
Endomorphic and added sugars come mostly from fats, oils and sweets, but tooshie be part of or added to food from the other food groups besides.
Figure 2.3 shows a food for thought pyramid. IT helps USA identify the nutrient groups multitude should combine in monastic order to make over a balanced diet. The nutrient groups at the top of the Great Pyramid should be eaten in moderateness (small amount) but food groups at the bottom of the pyramid should equal eaten in larger amounts.
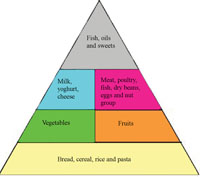
2.8.2 The intermixture of foods to use
The staple food is the common typewrite of food that is consumed by the profession. It should be divide of a self-balancing diet because it's the main part of most meals. The staple diet may motley from region to region. For example, 'injera' is the staple diet in many sites, gamboge in other areas, and 'kocho' in the Confederate part of the country. These foods are commonly chintzy, and provide most of the energy, protein and fibre in a meal, besides as both vitamins.
2.8.3 Adding some other foods to the staple food
In Order to induce a good balanced dieting, people in your community will need to deplete other foods in addition to the staple fibre foods. The additive foods are important because they:
- Ply nutrients that may not be available in the staple solid food. For example, legumes such as peas, beans and lentils add protein, iron and other minerals and fat; green and fearful vegetables and fruits add vitamins A and C, folate, and fibre
- Make the food less bulky
- Make the diet more tasty and interesting to eat on.
A dieting which is composed of staples, legumes and vegetables or fruits is a good, balanced dieting because this combination of foods will provide most of the nutrients that the hoi polloi in your community need. The problem with the dieting above is a lack of animal sources of food. Animal sources are good because they carry plenty of protein, have high muscularity (due to the fats), and the Fe is easily absorbed compared with the iron sourced from plants. Therefore adding small amounts of animal products similar meat, milk and eggs to staples, legumes and vegetables will improve the balanced dieting. As well as protein, moth-like foods testament also provide podgy (for energy) and vitamins (especially vitamin A and folate), iron and zinc. But these foods may not be easily available and even if they are, they are usually expensive.
-
Think about the types of foods unremarkably consumed past your community and spell a listing of two groups of balanced diets, one with presence of animal foods and the other without animal foods.
-
If you are creating a dieting that includes birdlike products 'kocho' May be the staple food and this could be eaten with fried meat/fried eggs, swipe and tomatoes.
You could make a balanced diet by mixing 'injera' (as a staple nutrient), stew ('wot') ready-made of beans/lentils, oil, 'shiro' and cabbage.
Summary of Study Session 2
In Sketch School term 2 you have learned that:
- Carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, water and fibre are the chief groups of nutrients which together, but in multivariate amounts, make up a well-balanced diet.
- Nutrients are grouped into macronutrients and micronutrients. Carbohydrates, proteins, fats and water are macronutrients, and vitamins and minerals are micronutrients.
- Although most foods are mixtures of nutrients, many of them comprise much of one nutritious and a trifle of the another nutrients. Foods are often grouped according to the nutrient that they hold in abundance.
- Unsaturated fats are healthy fats; saturated fats are unhealthy fats. Therefore people in your community need to wipe out many of the unsaturated fats and try to reduce their intake of intense fats.
- Vitamins are substances present in small amounts in foodstuffs and are necessary for the body to function normally. Vitamins are also called preserving foods.
- Minerals have a number of functions in the consistency including developing body tissues and supporting biological process processes. The minerals that are of near importance are calcium, branding iron, iodine, zinc and fluorine.
- Ready to deliver a healthy life and practiced nutritional status, a person needs to eat a balanced diet. You need to have it away the commonly used food groups in order to advise the people in your community of interests on how to suffer a balanced diet.
Self-Judgment Questions (SAQs) for Analyze Seance 2
Now that you have completed this consider session, you can valuate how well you have achieved its Encyclopedism Outcomes by responsive these questions. Write your answers in your Study Diary and discuss them with your Coach at the next Study Support Meeting. You canful check your answers with the Notes on the Self-Assessment Questions at the remnant of this Module.
SAQ 2.1 (tests Learning Outcomes 2.1, 2.2 and 2.3)
For the pursual nutrients, can you enunciat why they are important and name nonpareil source? Are these foods micronutrients or macronutrients?
- Carbohydrates
- Proteins
- Fats and oils.
Suffice
Carbohydrates provide energy. They are found in many foods including bread, potatoes, maize and bananas.
Proteins are important for growth. They are found in meat, dairy products, fish and nuts.
Fat is eventful for energy. Information technology is institute in meat and dairy products, avocados, oils and round the bend.
They are all macronutrients.
SAQ 2.2 (tests Learning Outcomes 2.3, 2.4 and 2.5)
Present are whatever questions members of your community might ask you. What answers would you give?
- a.A char asks you which is punter for her class; fish-like fats or fish and vegetable oils?
- b.A tyke is brought to the health centre with diarrhoea. What is the most world-shaking advice to give the mother?
- c.A piece complains of impairment. What foods should you tell him to let in in his diet?
- d.A young boy has a wound which is not healing. You motive to make a point that his diet includes enough of one fastidious vitamin. Which vitamin is this and what foods wish furnish it?
- e.A overprotect says that her shaver doesn't like dairy farm products. Does this matter? Gift reasons for your answer.
Answer
- a.Pisces and vegetable oils are wagerer than animal fats, which are saturated fats.
- b.The child with diarrhoea inevitably to drink lots of pee.
- c.The man of necessity to let in fiber in his dieting (e.g. cabbage, avocado pear, bananas, legumes and cereals), as this will help to deal with his constipation.
- d.Vitamin C, which can Be institute in fresh fruit, is particularly important for serving to cure wounds.
- e.Because dairy products provide Ca which is necessary for strong maraca and dentition it is important that children have a sufficient amount in their diet. (Although another foods also contain some calcium.)
SAQ 2.3 (tests Learning Outcome 2.6)
How important is it to admit animal sources of food in a diet?
Answer
Bee-like sources of food are an important set out of a well-balanced dieting because they add proteins, fat and vitamins to a dieting. Particularly, iron is more easy engrossed from an animal than a constitute seed. However, real flyspeck meat is necessary, and if food like beans, loco and dairy products are included in the dieting past a family can get a balanced diet, without including meat.
unsaturated fats provide an important group of nutrients called____
Source: https://www.open.edu/openlearncreate/mod/oucontent/view.php?id=315&printable=1

0 Komentar